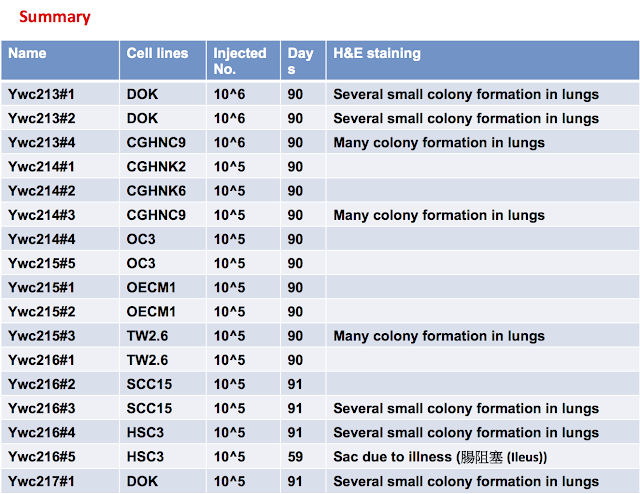
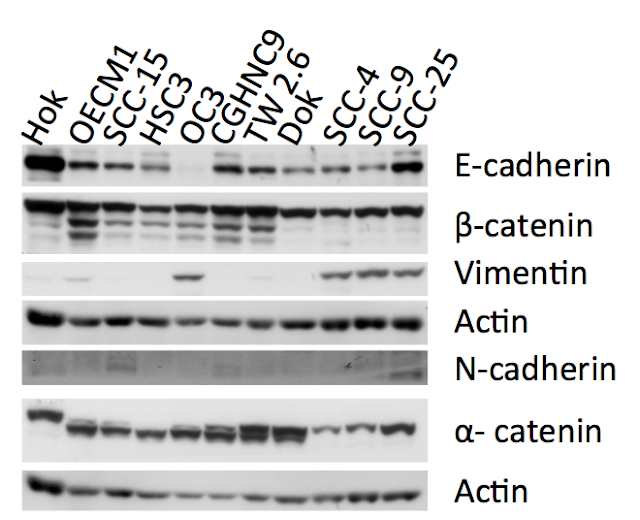
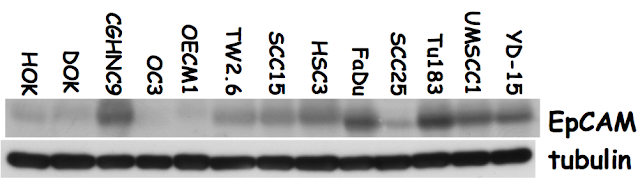
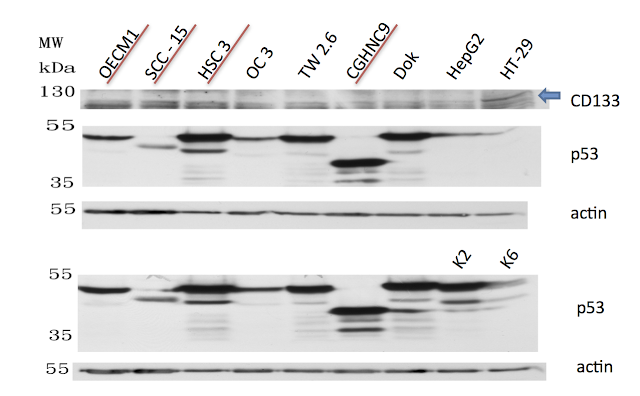
由 sufang 在 四, 03/27/2014 – 00:00 發表 Oral Cancer Arecoline DOK nicotine NNK
OrCa小組會議 (03/27/2014)
素芳的筆記本:
- nicotine: 500 uM
- NNK: 10 uM
- arecoline (AC): 50 uM or 100 uM
- treated for ~ 1 year, looking for carcinoge-tolerant cell clones, eg. NNK4, NNK5, NNK6, NIC4, NIC5, NIC6
- doubling time
- migration assay
- In vivo tumorigenesis
- Expression array analysis (“Merged_Kuo_Shiah” from Jonhson on 4/18/2014)
- from 靜娟 (第一次DOK1等七片arrray, 第二次DOK2等三片arrray)
- DOK pool 1 (DOK1)
- NIC4 (NIC4)
- NIC5 (NIC5)
- NIC6 (NIC6)
- NNK4 (NNK4)
- NNK5 (NNK5)
- NNK6 (NNK6)
- ——————————————
- DOK pool 2 (DOK2)
- AC50 pool (AC50)
- AC100 pool (AC100)
- from 夏博 (5片arrray, S=Shiah, QN=quantile normalization):
- Dok (DOK3)
- Arecoline 50 uM 5-day (AC50_short)
- Arecoline 50 uM 12-mo (來自靜娟;命名為 AC50_1)
- NNK 10 uM 5-day (NNK_short)
- NNK6 12-mo (來自靜娟;命名為 NNK6_1)
- from 靜娟 (第一次DOK1等七片arrray, 第二次DOK2等三片arrray)
- ARE: anti-oxidant responsive element; Nrf2/ARE
- NRF2=NFE2L2
- KEAP1 (E3 ligase adaptor)
- AKR1C2, C3, C4
- SOD1, 2, 3
- nAchRa9
#1由 sufang 在 三, 04/30/2014 – 22:50 發表。
YES!
把Johnson給的merge data灌進去仲彥的MOLAS portal了 (共有18,056 unique genes)! 大家自行探險一下~ (05/05 updated)
user name: sflin1@gmail.com
psswd: sflin123
註一: 各片array代號請見上面主文紫色字部份。
#2由 EVKVLIN 在 一, 04/28/2014 – 11:15 發表。
靜娟播放Slides
原始powerpoint file. (dok_model_jing_juan_.pptx)
_________
#3由 EVKVLIN 在 三, 04/16/2014 – 11:34 發表。
DOK info from Ya-Wen
#4由 sufang 在 五, 05/02/2014 – 20:20 發表。
兩篇文獻放在最下面
PLoS One. 2013 Dec 27;8(12):e83479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083479. eCollection 2013.
Clinical significance of Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Huang CF1, Zhang L1, Ma SR1, Zhao ZL1, Wang WM1, He KF1, Zhao YF2, Zhang WF2, Liu B2, Sun ZJ2.
Huang CF1, Zhang L1, Ma SR1, Zhao ZL1, Wang WM1, He KF1, Zhao YF2, Zhang WF2, Liu B2, Sun ZJ2.
Abstract
Oxidative stress has been reported to play an important role in progression and prognostication in various kinds of cancers. However, the role and clinical significance of oxidative stress markers Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has not been elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the correlation of oxidative stress markers Keap1 and Nrf2 expression and pathological features in OSCC by using tissue microarray. Tissue microarrays containing 17 normal oral mucosa, 7 oral epithelial dysplasia and 43 OSCC specimens were studied by immunohistochemistry. The association among these proteins and pathological features were analyzed. Expression of oxidative stress markers Keap1, Nrf2, and antioxidants PPIA, Prdx6, as well as CD147 was found to increase consecutively from normal oral mucosa to OSCC, and the Keap1, Nrf2, PPIA, Prdx6, CD147 expression in OSCC were significantly higher when compared to normal oral mucosa. Expression of Keap1, Nrf2 in tumors was not found to be significantly associated with T category, lymph node metastases, and pathological grade. Furthermore, we checked the relationship among these oxidative stress markers and found that Keap1 was significantly correlated with Nrf2, Prdx6 and CD147. Significant relationship between Nrf2 and Prdx6 was also detected. Finally, we found patients with overexpression of Keap1 and Nrf2 had not significantly worse overall survival by Kaplan-Meier analysis. These findings suggest that ROS markers are associated with carcinogenesis and progression of OSCC, which may have prognostic value and could be regarded as potential therapeutic targets in OSCC. PMID: 24386210
Mol Cell. 2014 Mar 20;53(6):916-28. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.01.033. Epub 2014 Mar 6.
Nrf2 Amplifies Oxidative Stress via Induction of Klf9.
Zucker SN1, Fink EE1, Bagati A1, Mannava S1, Bianchi-Smiraglia A1, Bogner PN2, Wawrzyniak JA1, Foley C1, Leonova KI1, Grimm MJ3, Moparthy K1, Ionov Y4, Wang J5, Liu S5, Sexton S6, Kandel ES1, Bakin AV4, Zhang Y7, Kaminski N8, Segal BH3, Nikiforov MA9.
Nrf2 Amplifies Oxidative Stress via Induction of Klf9.
Zucker SN1, Fink EE1, Bagati A1, Mannava S1, Bianchi-Smiraglia A1, Bogner PN2, Wawrzyniak JA1, Foley C1, Leonova KI1, Grimm MJ3, Moparthy K1, Ionov Y4, Wang J5, Liu S5, Sexton S6, Kandel ES1, Bakin AV4, Zhang Y7, Kaminski N8, Segal BH3, Nikiforov MA9.
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) activate NF-E2-related transcription factor 2 (Nrf2), a key transcriptional regulator driving antioxidant gene expression and protection from oxidant injury. Here, we report that in response to elevation of intracellular ROS above a critical threshold, Nrf2 stimulates expression of transcription Kruppel-like factor 9 (Klf9), resulting in further Klf9-dependent increases in ROS and subsequent cell death. We demonstrated that Klf9 independently causes increased ROS levels in various types of cultured cells and in mouse tissues and is required for pathogenesis of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Mechanistically, Klf9 binds to the promoters and alters the expression of several genes involved in the metabolism of ROS, including suppression of thioredoxin reductase 2, an enzyme participating in ROS clearance. Our data reveal an Nrf2-dependent feedforward regulation of ROS and identify Klf9 as a ubiquitous regulator of oxidative stress and lung injury. PMID: 24613345.