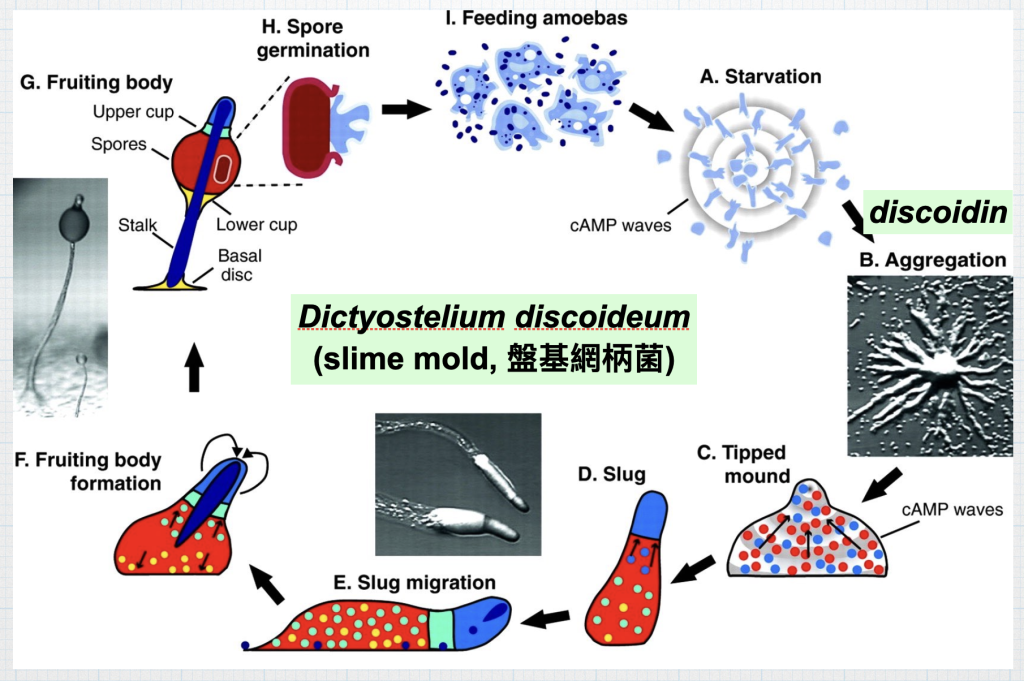
The discoidin domain is responsible for slime mode aggregation
The Tang Lab (成大湯銘哲老師)
2005 Wang et al., Function of discoidin domain receptor I in HGF-induced branching tubulogenesis of MDCK cells in collagen gel (15468059) 2006 Wang et al., A discoidin domain receptor 1/SHP-2 signaling complex inhibits alpha2beta1-integrin-mediated signal transducers and activators of transcription 1/3 activation and cell migration (16611743)
2009 Yeh et al., RDiscoidin domain receptor 1 activation suppresses alpha2beta1 integrin-dependent cell spreading through inhibition of Cdc42 activity (18780290)
2009 Wang et al., DDR1/E-cadherin complex regulates the activation of DDR1 and cell spreading (19474292)
2010 Eswaramoorthy et al., DDR1 regulates the stabilization of cell surface E-cadherin and E-cadherin-mediated cell aggregation (20432435)
2011 Yeh et al., DDR1 triggers epithelial cell differentiation by promoting cell adhesion through stabilization of E-cadherin (21289093)
2012 Yeh et al., A tale of two collagen receptors, integrin beta1 and discoidin domain receptor 1, in epithelial cell differentiation (23015544)
2019 Yeh et al., Dichotomy of the function of DDR1 in cells and disease progression (30954568)
The Sahai Lab (G-Scholar)
2007 Gaggioli et al., Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells (18037882)
2011 Hidalgo-Carcedo et al., Collective cell migration requires suppression of actomyosin at cell-cell contacts mediated by DDR1 and the cell polarity regulators Par3 and Par6 (21170030)
2014 Hirata et al., Retrograde flow of cadherins in collective cell migration (24981633)
Our Lab (G-Scholar)
2012 蔡宛樺 et al., Overexpression of Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 (DDR1) in oral squamous cell carcinoma (Poster @ EORTC-NCI-AACR molecular targets and cancer therapeutics symposium)
2019 Chou et al., MicroRNA-486-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in oral cancer by targeting DDR1 (31253192)
2020 陳玉蓮 et al., Discoidin Domain Receptor-1 (DDR1) is Involved in Angiolymphatic Invasion in Oral Cancer (32244515)

People who cited our DDR1 paper! (GoogleTrack)
2024/06/28 Differential transcriptional invasion signatures from patient derived organoid (POD) models define a functional prognostic tool for head and neck cancer (Oncogene PubMed) (=pdf6181_)
Notebooklm: This scientific article investigates how different invasion patterns in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) affect patient outcomes. Researchers created patient-derived organoid (PDO) models that mimicked collective invasion, where cells invade as a group, and single-cell invasion. By analyzing gene expression, the study found that collective invasion is associated with increased activity of the YAP protein, a key regulator of cell growth and movement. Moreover, a collective invasion gene signature, identified by the researchers, was linked to poorer survival rates in HNSCC patients. This research highlights the importance of understanding invasion patterns in cancer and suggests that targeting collective invasion mechanisms, potentially through YAP, could lead to new treatment strategies. (跟我們較不同的地方是檢體為舌癌組織及腮腺癌 parotid gland)
Figure 5 及 Table 1 highlight the gene signatures distinguish collective invasion (e.g. CLDN1, IGFBP2, PDPN, CSF2, THBS1), vs. single cell invasion (e.g. CXCL1, IL33)